All Resources
Europa Ice Floes
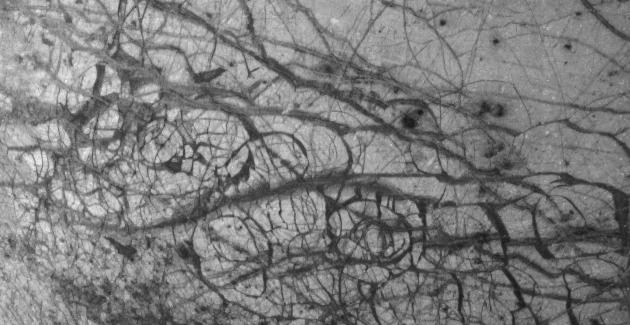
Jupiter's moon Europa, as seen in this image taken June 27, 1996 by NASA's Galileo spacecraft, displays features in some areas resembling ice floes seen in Earth's polar seas. Europa, about the size of Earth's moon, has an icy crust that has been severely fractured, as indicated by the dark linear, curved, and wedged-shaped bands seen here. These fractures have broken the crust into plates as large as 18.5 miles (30 kilometers) across. Areas between the plates are filled with material that was probably icy slush contaminated with rocky debris. Some individual plates were separated and rotated into new positions. Europa's density indicates that it has a shell of water ice thicker than about 60 miles (100 kilometers), parts of which could be liquid. Currently, water ice could extend from the surface down to the rocky interior, but the features seen in this image suggest that motion of the disrupted icy plates was lubricated by soft ice or liquid water below the surface at the time of disruption. This image covers part of the equatorial zone of Europa and was taken from a distance of bout 96,300 miles (156,000 kilometers) by the Solid-state Imaging Subsystem on the Galileo spacecraft. North is to the right and the sun is nearly directly overhead. The area shown is about 310 by 600 miles (510 by 989 kilometers), and the smallest visible feature is about 1 mile (1.6 kilometers) across.