What makes us think that Europa has an ocean?
Europa and her three large sibling satellites - Io, Ganymede and Callisto - were discovered by the astronomer Galileo in 1610, but nearly 400 years passed before any detailed views of their surfaces were seen and the uniqueness of these "Galilean" moons was revealed. In the 1960s, ground-based telescope observations determined that Europa's surface composition is mostly water ice, as are most other solid bodies of the outer solar system.
The Pioneer 10 and 11 spacecraft flew by Jupiter in the early 1970s, but the first spacecraft to image the surfaces of Jupiter's moons in significant detail were the Voyager 1 and 2 spacecraft. Voyager 1's closest approach to Jupiter occurred in March 1979, with Voyager 2 following in July of the same year. The best imaging resolution of the Voyagers was limited to just over 1 mile (2 kilometers) per pixel. These images revealed a surface brighter than that of Earth's moon, crisscrossed with numerous bands and ridges, and with a surprising lack of large impact craters, tall cliffs or mountains (in other words, a very smooth surface, relative to the other icy moons).
Even though the Voyagers did not pass extremely close to Europa, their images were of high enough quality that researchers noted some of the dark bands had opposite sides that matched each other extremely well, like pieces of a jigsaw puzzle. These cracks had separated, and dark, icy material appeared to have flowed into the opened gaps, suggesting that the surface had been active at some time in the past. Voyager images showed only a handful of impact craters, which are expected to build up over time as a planetary surface is constantly bombarded by meteorites over billions of years until the surface is covered in craters. Thus, a lack of large impact craters suggested that the moon's surface was relatively young and implied that something had erased them - such as icy, volcanic flows, or settling of the icy crust under its own weight.
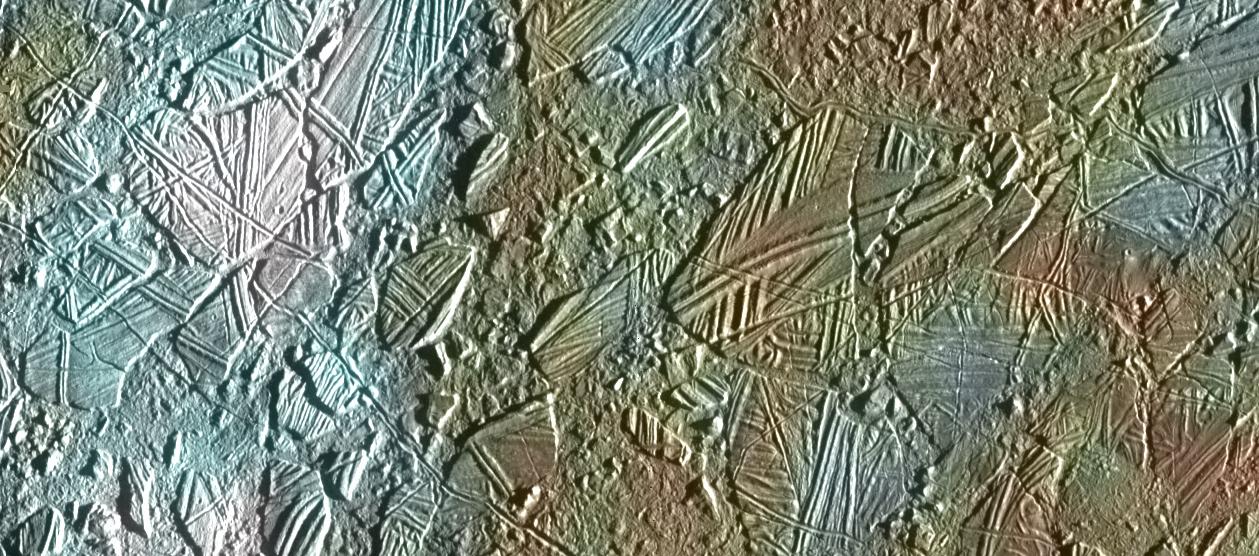

Scientists also found that the patterns of some of the longest linear features on the surface did not fit predicted patterns of fractures that should be created by tides as Europa orbits Jupiter. They determined that the patterns would fit very well if Europa's surface could move independently and was not locked to the rest of the interior, as would be the case if a layer of liquid or slightly warmer ice existed between the crust and deep interior.
There also were tantalizing hints that perhaps Europa had a warm interior at some time in the past, and perhaps still does. Studies of how tidal heating should affect Europa suggested that a global subsurface ocean might exist within the icy moon today.
These intriguing findings led to a strong sense of anticipation for the Galileo mission, which launched in 1989 and entered orbit around Jupiter in 1995. Galileo's primary mission included observations of each the four Galilean satellites during repeated flybys. The information about Europa that Galileo sent was so intriguing that the mission was extended to make a total of 12 close flybys of the icy moon. Data from the mission included images of Europa at a range of scales, revealing new details about the surface and providing context for how those details related to the moon as a whole.
One of the most important measurements made by the Galileo mission showed how Jupiter's magnetic field was disrupted in the space around Europa. This measurement strongly implied that a special type of magnetic field is being created (induced) within Europa by a deep layer of some electrically conductive fluid beneath the surface. Based on Europa's icy composition, scientists think the most likely material to create this magnetic signature is a global ocean of salty water.
Europa Clipper will seek to confirm the presence of its ocean. For example, measurements of the amount of flexing due to the tides are one important indicator -- if the ocean exists, the tides should deform the surface by about 30 m (100 feet); if the moon is frozen through, the tides should stretch the surface by only one meter (3 feet). Also of great interest will be the composition of the reddish material on the surface. Scientists would like to know if this material holds clues to the composition of the ocean and whether material is cycling between the surface and the interior.
In addition to Europa Clipper, other missions will explore Europa. The Jupiter Icy Moons Explorer (JUICE) by the European Space Agency (ESA) will address some of these questions, and conduct detailed investigations of Europa's sister moon, Ganymede.
In addition, the proposed Europa Lander mission concept would land on Europa’s surface to perform an in situ study of composition and habitability.